< Previous | Contents | Next >
![]()
For each type of child restraint, there are many different models available. When purchasing a child restraint, be sure it is designed to be used in a
motor vehicle. If it is, the restraint will have a label saying that it meets
federal motor vehicle safety standards.
The restraint manufacturer's
instructions that come with the
restraint state the weight and height limitations for a particular child
restraint. In addition, there are many kinds of restraints available for
children with special needs.

{ Warning
To reduce the risk of neck and head injury in a crash, infants and
toddlers should be secured in a
rear-facing child restraint until age two, or until they reach the
maximum height and weight limits of their child restraint.

{ Warning
A young child's hip bones are still so small that the vehicle's regular seat belt may not remain low on
the hip bones, as it should. Instead, it may settle up around the child's
abdomen. In a crash, the belt would apply force on a body area that is
unprotected by any bony structure.
This alone could cause serious or fatal injuries. To reduce the risk of serious or fatal injuries during a
crash, young children should always be secured in appropriate child
restraints.
![]()
Child Restraint Systems
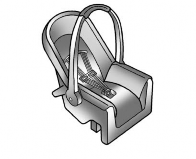
Rear-Facing Infant Restraint
A rear-facing child restraint provides restraint with the seating surface
against the back of the infant.
The harness system holds the infant in place and, in a crash, acts to keep
the infant positioned in the restraint.
SEATS AND RESTRAINTS 101
![]()
![]()
![]()
Securing an Add-On Child Restraint in the Vehicle

{ Warning
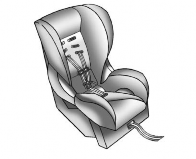
Forward-Facing Child Restraint
A forward-facing child restraint
provides restraint for the child's body with the harness.
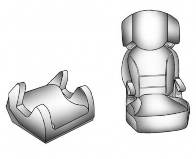
Booster Seats
A belt-positioning booster seat is used for children who have outgrown their
forward-facing child restraint.
Boosters are designed to improve the fit of the vehicle's seat belt system
until the child is large enough for the vehicle seat belts to fit properly
without a booster seat. See the seat belt fit test in Older Children 0 96.
A child can be seriously injured or killed in a crash if the child
restraint is not properly secured in the vehicle. Secure the child
restraint properly in the vehicle using the vehicle’s seat belt or
LATCH system, following the
instructions that came with that
child restraint and the instructions in this manual.
To help reduce the chance of injury,
the child restraint must be secured in the vehicle. Child restraints must be
secured in vehicle seats by lap belts or the lap belt portion of a lap-shoulder
belt, or by the LATCH system. See
Lower Anchors and Tethers for Children (LATCH System) 0 103 for more
information. Children can be
endangered in a crash if the child
restraint is not properly secured in the vehicle.